Evaluate customer experience: qualitative vs quantitative
Published on October 10, 2023 - Updated on December 19, 2023
Evaluate customer experience: qualitative vs. quantitative
Evaluate customer experience and customer journey is a key element of any business strategy focused on customer satisfaction and loyalty. In this endeavor, companies often turn to surveys to gather actionable data. However, there is a fundamental dilemma when designing these surveys: qualitative vs quantitative approach.
Qualitative vs Quantitative : what is the difference?
First and foremost, it's important to understand what these two terms refer to.
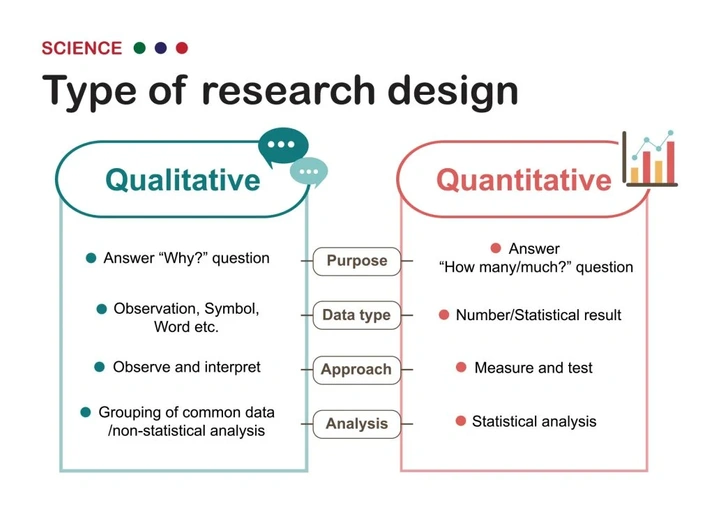
Quantitative method focuses on statistical data. It involves surveying a broad range of individuals, requiring a sufficient number of respondents and a sample constructed to represent your target audience.
Qualitative study, on the other hand, is a research methodology based on understanding the behaviors, needs, and perceptions of individuals.
While the quantitative approach aims to answer "who" or "what" questions, qualitative analysis seeks to explain "how" and "why."
Advantages and disadvantages
For qualitative data:
The qualitative measurement of customer experience allows for in-depth exploration of customer emotions, opinions, and experiences. The advantages lie in the ability to gather rich, nuanced, and contextual information about customer experiences. Qualitative interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys yield detailed narratives, help identify specific pain points, and provide insights into customer motivations. This enables companies to take more precise actions to improve the customer experience.
However, collecting and analyzing qualitative data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Additionally, subjective interpretation of responses can vary among researchers, making comparison and generalization more complex. Moreover, qualitative data is generally not as easy to quantify as quantitative data, making it challenging to track trends on a large scale.
For quantitative data:
Quantitative measurement of customer experience offers a structured, numerical approach to evaluating satisfaction and performance. The advantages include the ability to provide easily comparable data on a large scale. Key performance indicators (KPIs) like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) allow for quantifying customer satisfaction and loyalty, facilitating decision-making and trend tracking.
However, this approach may sometimes lack depth and fail to capture the complexity of individual emotions and experiences. It can also overlook the underlying reasons behind scores and specific pain points in the customer journey. Quantitative analysis can sometimes be perceived as impersonal, neglecting the details of customer interactions.

What are the methods for collecting these data?
Once you've made your choice regarding the type of data you want to obtain, it's time to collect it! There are numerous methods available, and the effectiveness of each can vary depending on your industry and customer base. Based on our experience, here are the most effective sources of data: For Qualitative Data:
- Interviews: face-to-face, phone, or online interviews.
- Focus groups: bringing together a small group of customers to discuss their experiences with a product or service.
- Participatory observation: researchers directly observe customers interacting with a product or service to understand their behavior and emotions.
- Content analysis: examining written comments, online reviews, and customer feedback to identify trends and themes.
- Open-ended surveys: using open-ended questions in surveys to allow customers to freely share their opinions and suggestions.
- Phone interviews: conducting semi-structured phone interviews to gather detailed customer feedback on their experiences.

For Quantitative Data:
- Structured surveys: using standardized surveys with multiple-choice questions or rating scales to quantify customer satisfaction and opinions.
- Analysis of existing data: using transactional data and internal databases to assess customer performance and retention.
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI) measurement: tracking metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), and Customer Effort Score (CES) to quantify customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Web navigation analysis: examining website navigation data to understand online customer behavior.
- Experience feedback analysis: utilizing data from customer feedback sources such as customer service calls, emails, or social media messages to quantify issues and concerns.
- Phone surveys: conducting quantitative phone surveys to assess customer satisfaction and opinions on a large scale.
- Big Data analysis: using massive data sets to identify trends and patterns in customer behavior.

Qualitative or quantitative study: which to use?
Qualitative and quantitative studies represent two complementary approaches in research. Generally, a qualitative study is conducted before a quantitative study to explore new opportunities or identify emerging issues.
Combining these two methods is often wise for surveys, market research, and other research endeavors. Qualitative study provides rich and detailed information on a specific topic. However, analyzing the results can be complex due to the diversity of expressions used by participants. Quantitative responses, on the other hand, offer numerical precision regarding each participant's responses.
By combining these methods, the overall quality of collected data is usually improved. It's essential to correctly distinguish between qualitative and quantitative studies and know when to transition from one to the other for effective research.
Are open-ended questions important to evaluate customer experience?
From our perspective as a company specializing in emotional analysis, it is crucial to highlight the essential role of open-ended questions in measuring customer experience.
Unlike closed-ended questions that limit customer responses to predefined choices, open-ended questions invite customers to freely and spontaneously share their thoughts, emotions, and suggestions. This enables capturing rich and detailed information about their experiences.
By asking open-ended questions in surveys and encouraging customers to share their thoughts more freely, companies can discover valuable insights. They can identify hidden pain points, moments of satisfaction, innovative ideas to improve products or services, and even emerging trends.
However, it's important to note that collecting and analyzing responses to open-ended questions can be more time and resource-intensive than quantitative methods. Advanced semantic analysis tools, such as those developed by us at Q°emotion, may be necessary to extract meaningful information from large amounts of unstructured text. Nevertheless, this investment is worthwhile as it allows companies to better understand and improve the customer experience by directly addressing customer concerns and needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, measuring customer experience is a crucial step for any business concerned with customer satisfaction and loyalty. The dilemma between qualitative and quantitative approaches offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, but the real value often lies in the combination of these complementary methodologies. Qualitative research delves into the depth of customer emotions and motivations, while quantitative analysis provides a structured overview on a large scale. Furthermore, the importance of open-ended questions in this endeavor cannot be underestimated as they enable capturing valuable and detailed information about the customer experience. Ultimately, a balanced approach tailored to the research objective is the key to continuously improving the customer experience and strengthening the trust relationship between the company and its customer base.
Similar posts
The 7 types of customers every business should know
Published on January 08, 2024 - Updated on February 06, 2024
Understanding your customer base Building a trusting relationship relies on a deep understanding of customer motivations. In this context, customer typology emerges as a segmentation tool aimed at mi...
How to calculate customer retention rate ?
Published on January 04, 2024 - Updated on January 09, 2024
How to calculate customer retention rate ? "There is only one boss in the company: the customer! And he can fire anyone, from the CEO to the simple employee, just by spending his money elsewhere." - ...